Do you know what FriedEx Ransomware is?
FriedEx is a vicious ransomware threat that targets home computer users and businesses for money extortion. The infection was detected in July 2017 and a month later it hit NHS hospitals in Scotland. Researchers determined that the threat was spread using RDP brute force attacks. The breach resulted in the cancellation of a small number of appointments, and the affected system were restored.
The FriedEx ransomware is also known as BitPaymer, sometimes spelled Bit Paymer. The malware has been investigated to find that its code resemble the code of the banking trojan Dridex. The Dridex malware is a trojan stealing bank credentials with the help of HTML injections. The trojan would access the targeted system through macros in Microsoft Office. The threat came to the spotlight in late 2014 and was considered as a new version of another banking trojan Cridex, which itself is based on the infamous Zeus malware.
The Dridex trojan is being developed and is updated periodically, implying that the authors behind the banking Trojan are not planning on abandoning their production. The most recent version of Dridex was released on December 14, 2017.
The FriedEx ramsomware has been found to use the same hiding techniques as Dridex, suggesting that the criminals are working enthusiastically to increase their target audience, which, in return, would bring bigger revenues.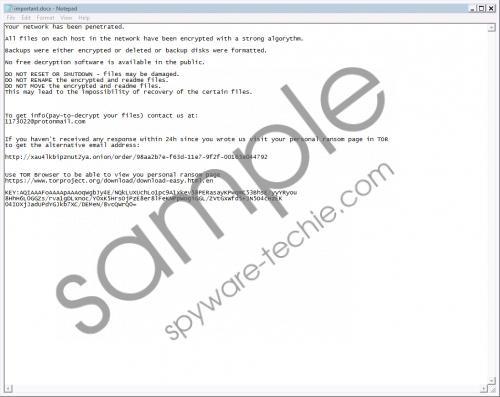 FriedEx Ransomware screenshot
FriedEx Ransomware screenshot
Scroll down for full removal instructions
As soon as the FriedEx ransomare gets on the computer, it encrypts files on all hard drive partitions and removable drives. Every affected file gets the extension .locked, which is known to be used by older versions of FriedEx. Additionally, the ransomware creates two randomly named folder in the %LOCALLAPPDATA% directory; however, the folder are deleted as soon as the decryption process ends. The ransomware removes itself as well, so all that you should worry about is how to prevent new malware and ransomware attacks.
To encrypt files, the ransomware uses a randomly generated RC4 cipher, which is encrypted afterwards by a 1024-RSA public key.
To frighten victims into paying for file decryption, the ransomware creates a .txt file informing victims about the issue and instructing them to contact the attackers at 1173022@protonmail.com. Unlike many other ransomware infections encrypting files, FriedEx’s ransom note does not specify what specific ransom fee has to be paid. This tactic suggests that the attackers would require different sums depending on how quickly a victim reacts to the ransom note. In any case, paying up would be unwise, because your encrypted files are not likely to be decrypted even if you submit the payment.
In case the attackers fail to reply to the victim’s inquiry within 24 hours, the victim is asked to install the TOR browser for contacting the crooks for more information.
We advise you against engaging with the gang behind the FriedEx ransomware, because they are not likely to help you restore your lost data. All that you would be asked is pay a considerable sum of money in some cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin. The variant of BitPaymer analyzed in August 2017 asked for 53 Bitcoin, which now would be almost $500,000.
Law enforcement institutions advise computer users against paying up and encourage them to take preventative measures so that similar instances do not occur again in the near future. One of the means to prevent data loss is making copies of valuable data to portable storage devices and keeping them unplugged. Additionally, it is important to keep the operating system updated and secured, and stay away from questionable online content, such as unrecognized emails and unreliable software sharing websites.
In non-techie terms:
FriedEx is a damaging infection encrypting files throughout the whole operating system. The infection spreads through RDP, so it is essential to use strong passwords to withstand RDP brute force attacks. The infection drops it ransom notes without the ransom fee in every affected directory and removes itself after having encrypted files.
